Claude Code’s Rapid AI Chatbot Development Goes Open Source#
In a remarkable display of artificial intelligence’s accelerating capabilities, the Claude Code CLI tool has reportedly developed a fully functional AI chatbot for a platform in an astonishing four hours. This rapid prototyping achievement underscores the transformative potential of advanced AI assistants in modern software development. The solution, already deployed in production, has been generously released as open source, inviting wider collaboration and adoption. Here are the key facts and implications surrounding this impressive development:
- Rapid Development Cycle: The project saw Claude Code CLI tasked with creating an AI chatbot for an internal platform and delivered a working solution within a mere four hours, demonstrating unprecedented speed in software creation.
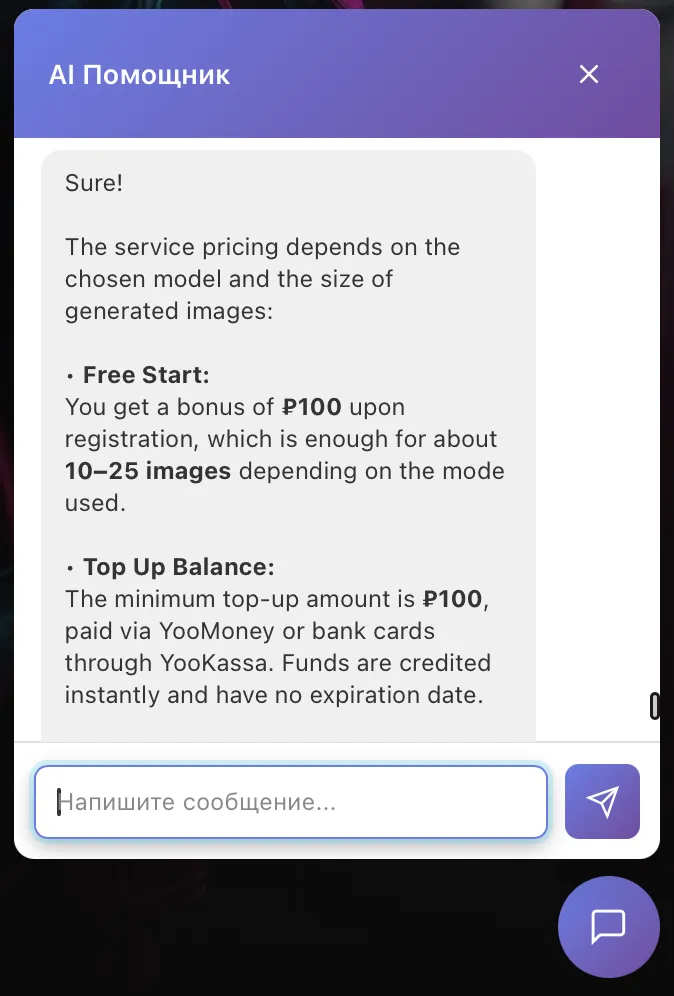
- Feature-Rich Solution: Despite the short development time, the resulting chatbot includes a context-dependent widget, a knowledge base built on Markdown files, direct escalation to Telegram for complex queries, and an automatic bug collection system.
- Production Readiness: The chatbot is not merely a prototype; it’s actively operating in a production environment, highlighting its stability and functional completeness straight out of its AI-driven development.
- Open-Source Contribution: The project has been made publicly available under an MIT license, with its source code hosted on GitHub (github.com/gmen1057/ai-chat-widget), fostering community development and transparency.
- Live Demo Available: A live demonstration of the widget’s capabilities is accessible at studio.jhunterpro.ru, where the chatbot can be found in the lower-right corner, allowing users to experience its functionality firsthand. This event marks a significant milestone in the evolution of AI-powered development tools. The ability of large language models like Claude Code to not just assist but autonomously build complex, production-ready applications in a matter of hours could redefine traditional software development workflows. This democratizes access to sophisticated AI solutions, potentially leveling the playing field for smaller teams and startups that lack extensive development resources. However, it also raises questions about quality assurance, the need for human oversight in critical systems, and the evolving role of human developers as AI takes on more of the coding burden. Looking ahead, this rapid development paradigm suggests a future where software engineering is less about writing code line-by-line and more about architecting systems, defining clear requirements, and intelligently leveraging AI tools. We can anticipate an explosion of niche, AI-generated applications, alongside a greater emphasis on prompt engineering and AI model fine-tuning as core developer skills. This shift promises to accelerate innovation across industries, drastically cutting time-to-market for new products and services, making technology more accessible and responsive than ever before.
